Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
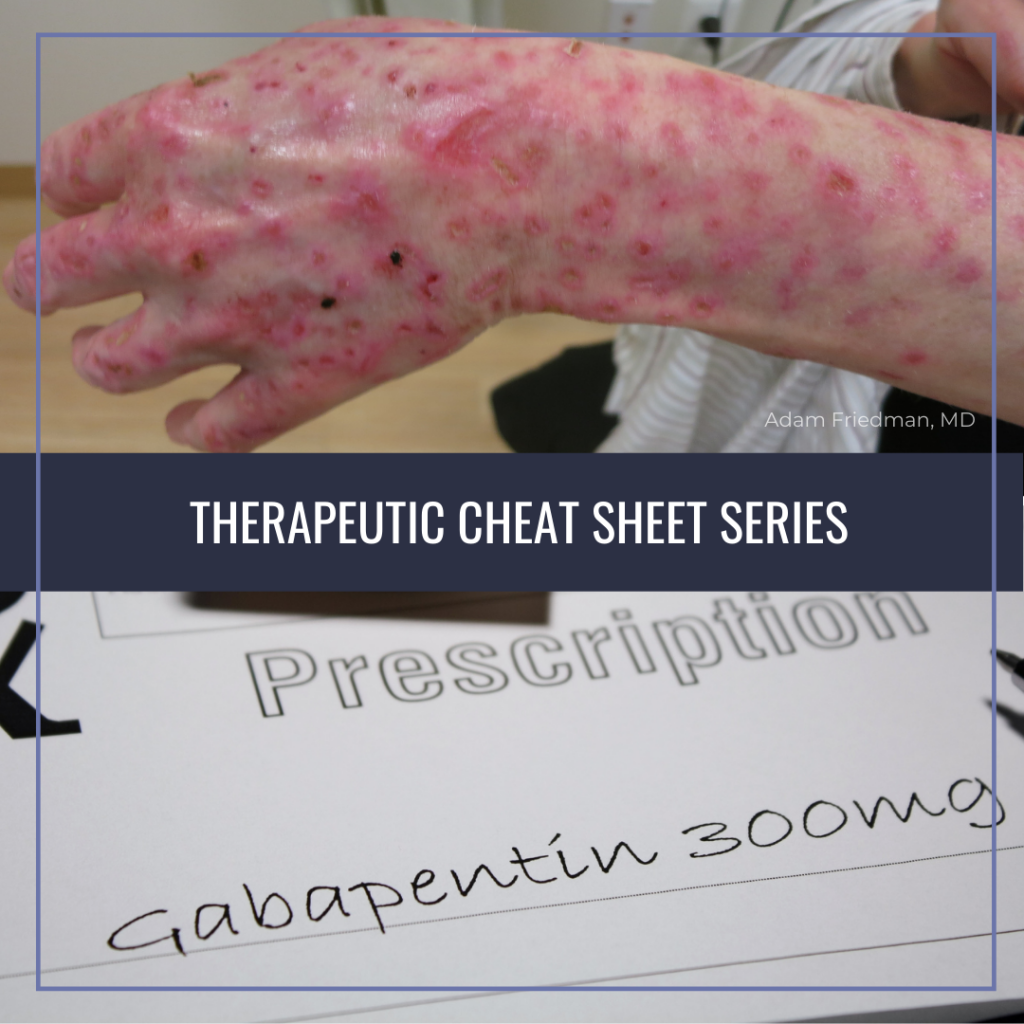
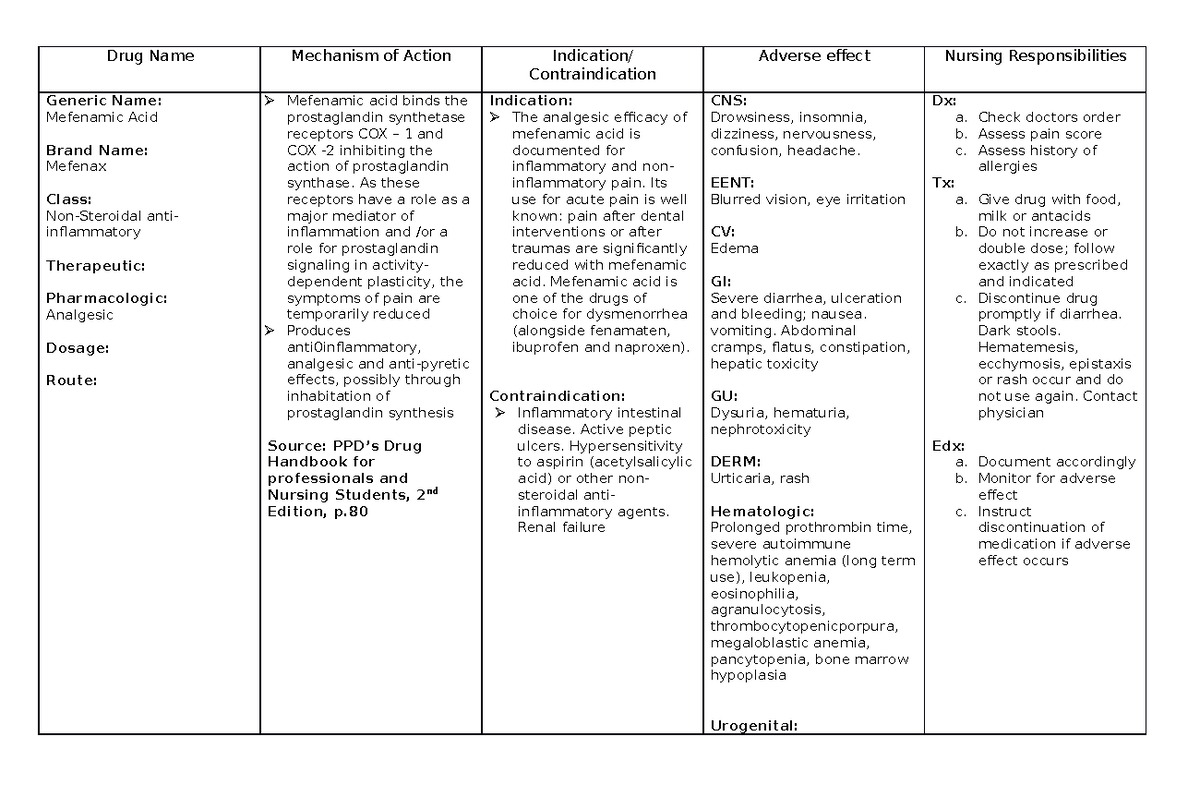
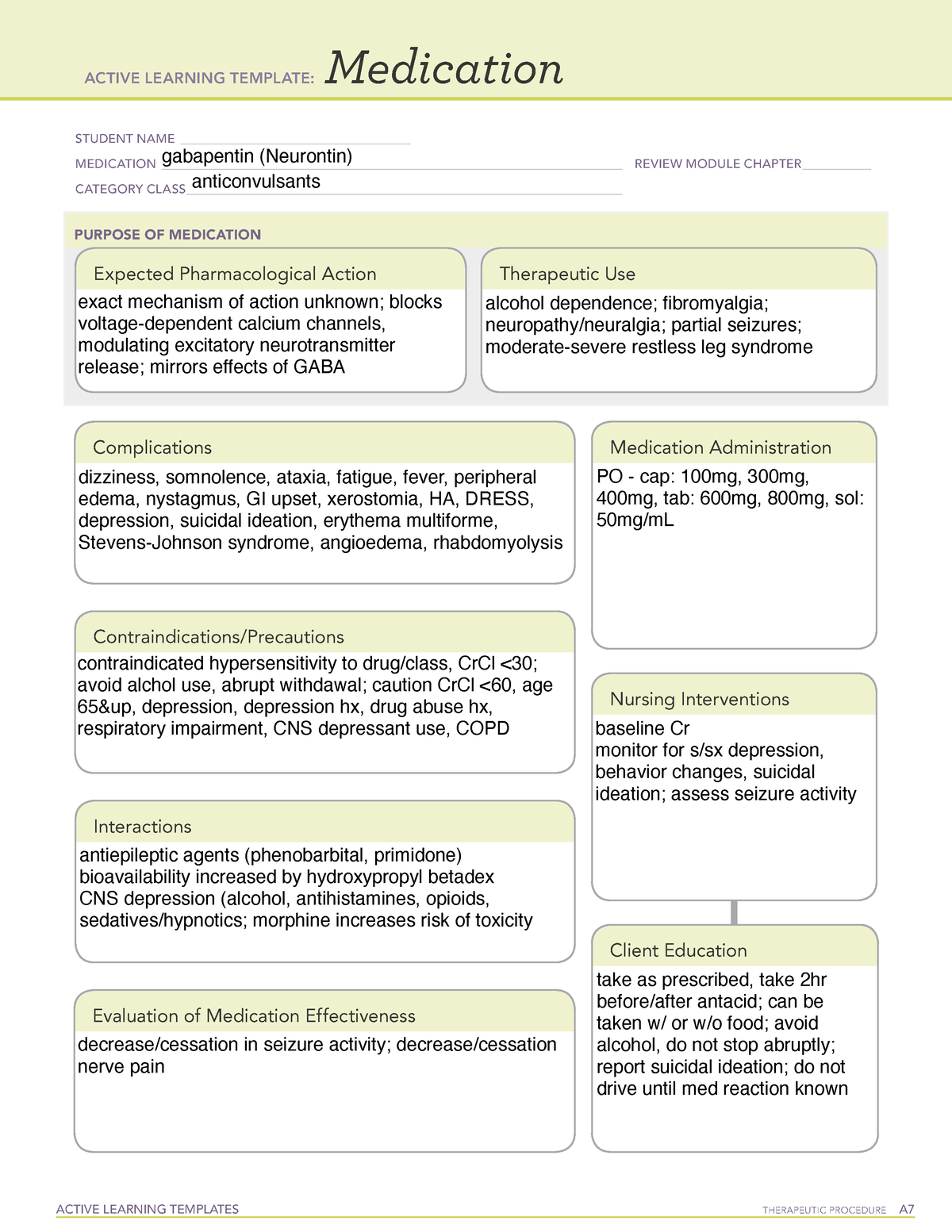
INTRODUCTION gabapentin (ga-ba- pen -tin) Neurontin Classification Therapeutic: analgesic adjuncts, therapeutic, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. Gabapentin is a gamma-amino acid that is cyclohexane substituted at position 1 by aminomethyl and carboxymethyl groups. Used for treatment of neuropathic pain and restless legs syndrome. It has a role as an anticonvulsant, a calcium channel blocker, an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin reference guide for safe and effective use from the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (AHFS DI). Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Generic name : Gabapentin Brand names: Neurontin® Gralise® (gabapentin extended release) Horizant® (gabapentin enacarbil) Therapeutic class: Anti-epileptic, Anticonvulsant Pharmacologic class: 1-amino-methyl cyclohexoneacetic acid, Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue FDA Approved: December 30, 1993 Chemical Formula: C9H17NO2 Pregnancy Gabapentin Medication Information Discover comprehensive details about Gabapentin, including its pronunciation, uses, dosage instructions, indications, and guidelines on how and when to take it or Gabapentin extended-release tablets (Horizant) are used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS; a condition that causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move the legs, especially at night and when sitting or lying down). Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Up to 14 characters (7 couplets) Divided into a therapeutic classification hierarchy As you increase the amount of couplets, more specific subgroup of drugs are being identified. Defines equivalent drug products having the same active ingredients, strength, route, form, and therapeutic use Example: 58-20-00-60-10-01-05 Nortriptyline HCL Capsule Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat seizures and nerve pain caused by the herpes virus. Includes Neurontin side effects, interactions and indications. Therapeutic Class Overview Neuropathic Pain Agents Therapeutic Class Overview/Summary: The agents approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of neuropathic pain include duloxetine (Cymbalta®), gabapentin (Neurontin®), gabapentin extended-release (Gralise®), gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant®), lidocaine patches (Lidoderm®) and pregabalin (Lyrica®).1-6 These agents ATC Group: N02BF01 Gabapentin The World Health Organization's ATC classification organizes medical drugs based on therapeutic properties, chemical composition, and anatomy. It helps make essential medicines readily available globally and is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is classified as an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain. Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Find detailed information on Gabapentin including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half-life, administration, and more. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Pharmacologic class: 1-amino-methyl cyclohexoneacetic acid. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant. Mechanism of action: Gabapentin helps to stabilize cell membranes by changing cation (sodium, calcium, and potassium) transport, reducing excitability, and suppressing seizure focus or discharge.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |