Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
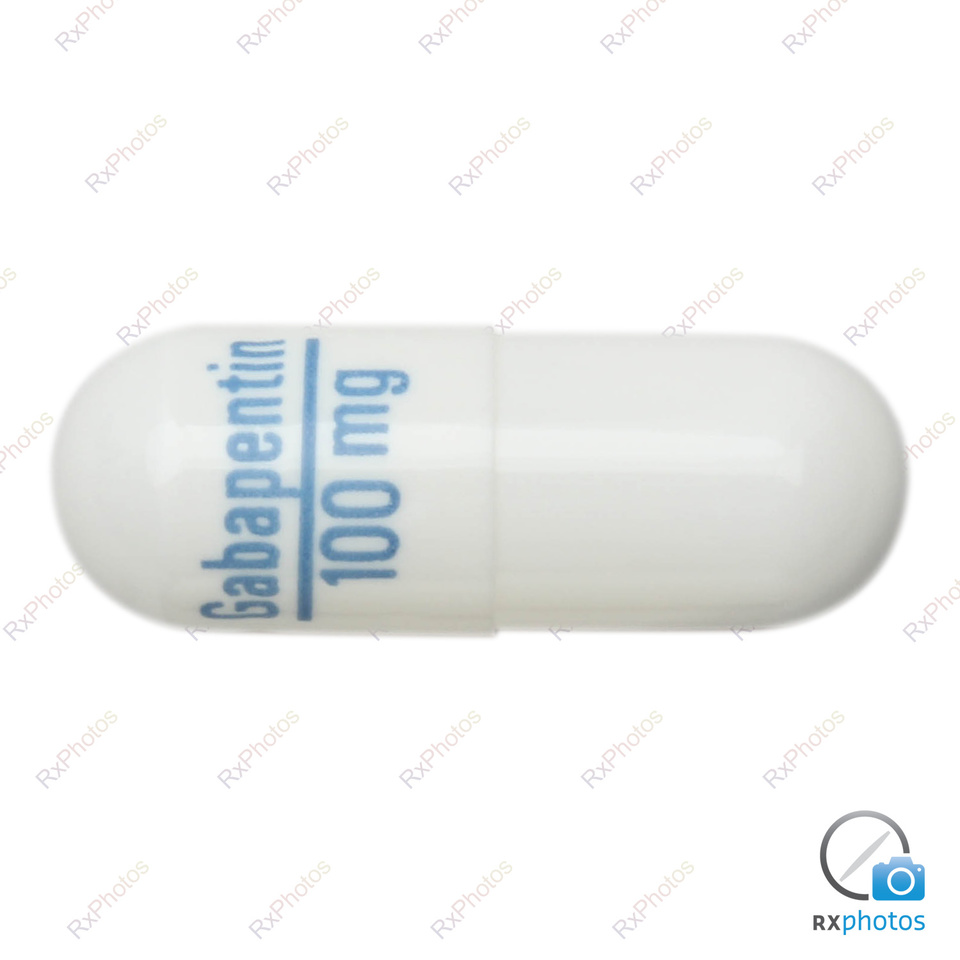
Gabapentin has also been associated with peripheral oedema,8 occurring in approximately 7% of people who take gabapentin.6 The risk is generally increased with older adults and with higher doses9, but a case of bilateral pitting oedema has occurred in a younger adult taking a relatively low (600mg/day) dose.10 Take special care especially if KEY PRACTICE POINTS: Gabapentin and pregabalin, known as gabapentinoids, are funded in New Zealand for use in people with neuropathic pain and for seizure control in some people with epilepsy Gabapentinoids should not be prescribed for people with chronic non-neuropathic pain, e.g. non-specific low back pain, and are no longer recommended for people with sciatica Response to gabapentinoids is Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Key Messages Gabapentin and pregabalin are indicated for the treatment of neuropathic pain only. Use in other types of pain is unapproved. Cases of abuse and dependence have been reported with gabapentin and pregabalin. Evaluate patients for a history of substance abuse and observe for signs of misuse or abuse. Concurrent treatment with CNS depressants (eg, opioids) and gabapentin or Further, gabapentin may be used in combination with other anti-epileptic drugs without concern for alteration of the plasma concentrations of gabapentin or serum concentrations of other anti-epileptic drugs. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. GABAPENTIN Other names: Arrow-Gabapentin®, Neurontin®, Nupentin® Important note: The following information is intended to add to, not replace, the knowledge and judgment of your doctor, pharmacist or other health care professional. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Unlike other agents in this class, it is not necessary to monitor gabapentin plasma concentrations to optimise NEURONTIN therapy. Further, NEURONTIN may be used in combination with other anti-epileptic drugs without concern for alteration of the plasma concentrations of gabapentin or serum concentrations of other anti-epileptic drugs. Gabapentin is used to treat and prevent some types of pain and seizures. It is also sometimes used for other conditions. Before you start Tell your doctor if you have kidney problems. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. How should you take it? Take gabapentin regularly as directed with a glass of Gabapentin is used to treat some types of nerve pain and epilepsy and prevent migraine headaches. Find out how to take it safely and possible side effects. Gabapentin is also called Neurontin or Nupentin. What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that is used to treat certain types of epilepsy. It is also used to treat neuropathic pain, a type of pain or altered sensation caused by damage to the nerves. Gabapentin is successfully being used to treat skin conditions associated with pain or pruritus of neuropathic origin. Gabapentin Medsurge is also used to treat neuropathic pain, a type of pain caused by damage to the nerves. This medicine belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin and pregabalin, known as gabapentinoids, are funded in New Zealand for use in people with neuropathic pain and for seizure control in some people with epilepsy. Key practice points: Gabapentin and pregabalin, known as gabapentinoids, are funded in New Zealand for use in people with neuropathic pain and for seizure control in some people with epilepsy Gabapentinoids should not be prescribed for people with chronic non-neuropathic pain, e.g. non-specific low back pain, and are no longer recommended for people with sciatica Response to gabapentinoids is Information for parents and carers about the use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). What Gabapentin does lepsy is a condition where you have repeated seizures (fits). There are Gabapentin is also used to treat neuropathic pain, a type of pain caused by damage to the nerves. This medicine belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Limited pharmacological treatment options to manage chronic non-neuropathic pain can lead to the inappropriate prescribing of gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin and pregabalin, known as gabapentinoids, are funded in New Zealand for use in people with neuropathic pain and for seizure control in some people with epilepsy. The benefit of gabapentinoids, even for conditions they are indicated Gabapentinoids-gabapentin & pregabalin This group of medications include both gabapentin and pregabalin. Both are use full for nerve related or neuropathic pain but can be used for other conditions. Both medications can cause some sedation, fuzzy thinking, unsteadiness and change in mood, but this tends to reduce in impact the longer these are Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |