Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
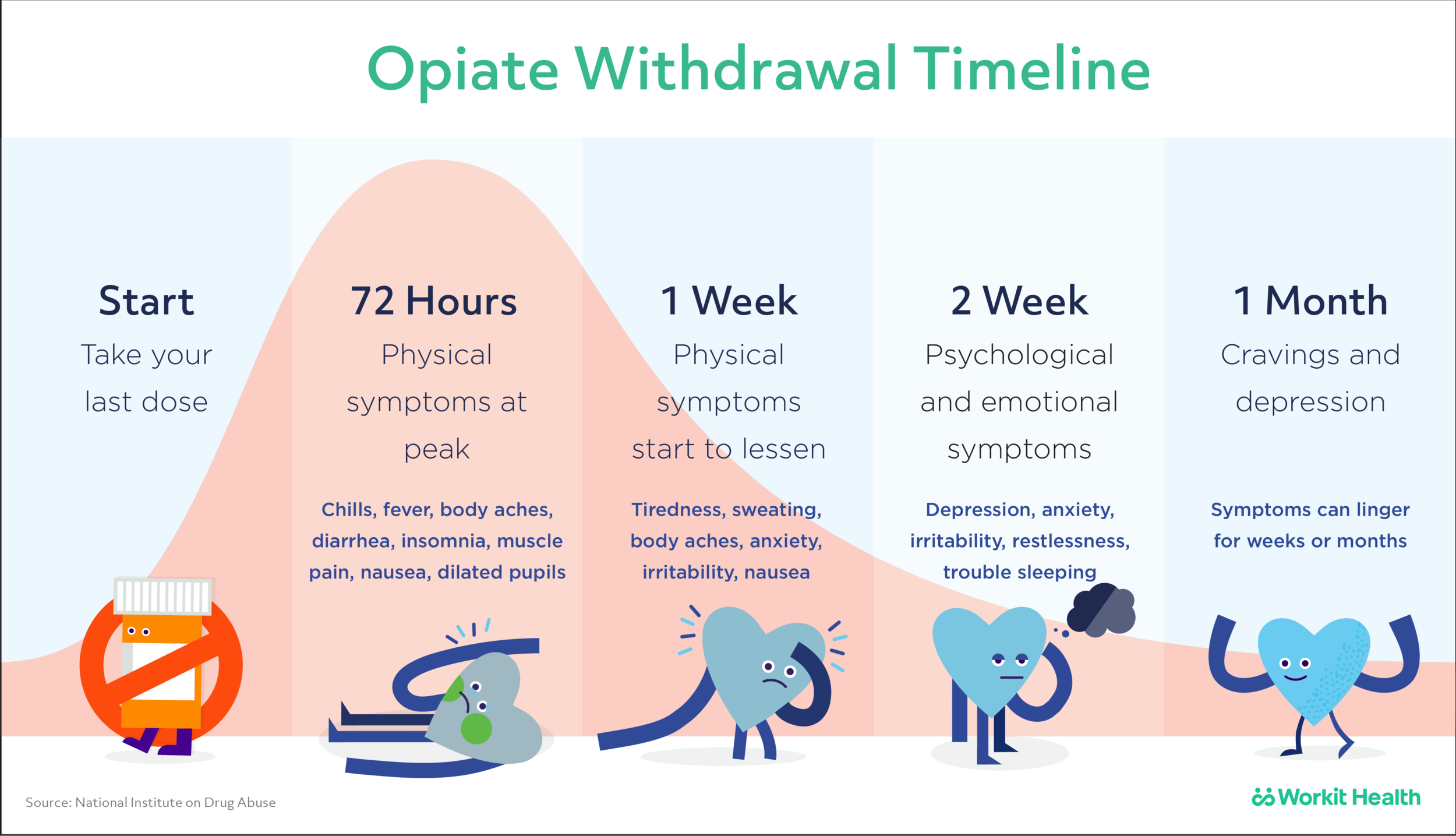
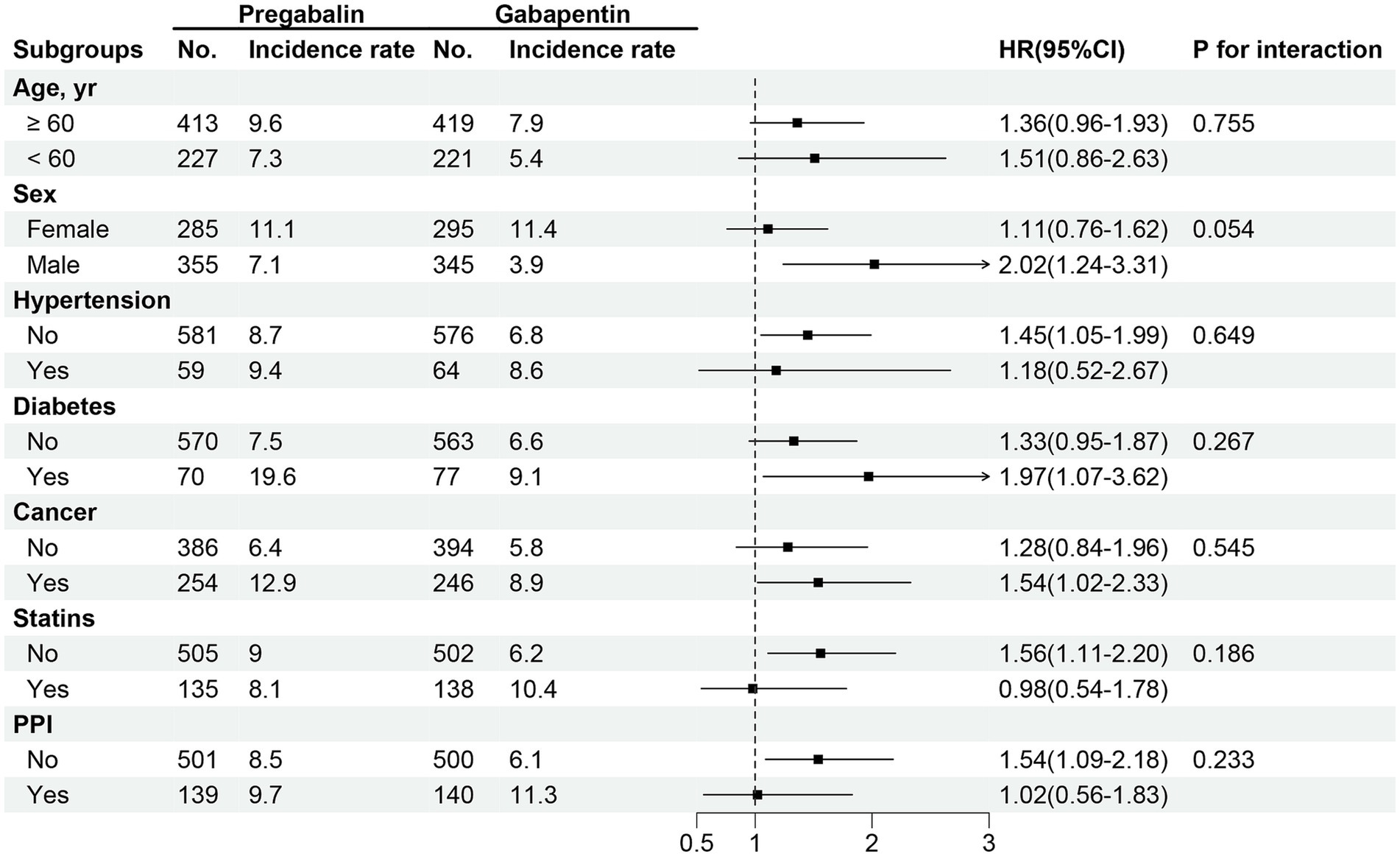
Considering the merits of ropivacaine, gabapentin, and clonidine, the present prospective double-blind randomized study was aimed to compare the clinical efficacy of oral gabapentin with clonidine as preemptive analgesic in knee arthroscopic repair, done under epidural anesthesia with 0.75% ropivacaine. A Moderate Drug Interaction exists between clonidine and gabapentin. View detailed information regarding this drug interaction. When it comes to **Clonidine vs Gabapentin**, the choice between these two medications ultimately depends on your individual needs and circumstances. If you're looking for a medication that can provide targeted relief from pain, Clonidine may be a good option. Oral gabapentin is more effective than oral clonidine as a premedication for providing postoperative analgesia in patients belonging to the age group of 18–65 years, ASA I and II, undergoing spinal anesthesia for surgery. The rescue analgesic requirement is also less in patients receiving gabapentin than clonidine. We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gabapentin and Clonidine. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 486,486 people who take Gabapentin and Clonidine, and is updated regularly. Oral clonidine is equally effective in producing preoperative sedation in comparison to oral gabapentin, while on the contrary oral clonidine is more efficacious in reducing laryngoscopic stress response than oral gabapentin. The present study is being done to investigate the effectiveness of oral clonidine premedication for attenuation of hemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation. Gabapentin, a structural analog of γ-aminobutyric acid, is used as an anticonvulsant drug. [10] Pretreatment with gabapentin can prevent the development of hyperalgesia. [11] We compared the effects of oral clonidine and gabapentin as premedicant in obtunding hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation in normotensive patients undergoing elective surgery. A total of 100 patients of either sex enrolled in the Medications to Treat Opioid Withdrawal Symptoms Sometimes medications can be used to help mitigate the symptoms of opioid withdrawal. These medications should be used sparingly and with caution. Ideally if the taper is slow enough, patients are experiencing minimal and tolerable opioid withdrawal and don’t need adjunctive medication. Be wary of using addictive medications, like Oral gabapentin at a dosage of 600 mg demonstrates superior efficacy as a premedication compared to oral clonidine 100 mcg for patients undergoing lower abdominal and lower limb surgeries under spinal anesthesia. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening Numerous reports in the medical literature and popular media have discussed the effectiveness of various nonhormonal agents in reducing menopausal hot flash symptoms. Data for these therapies are Oral clonidine is equally effective in producing preoperative sedation in comparison to oral gabapentin, while on the contrary oral clonidine is more efficacious in reducing laryngoscopic stress response than oral gabapentin. Clonidine Multiple studies demonstrate modest improvement in hot flashes with clonidine. 10, 11, 23, 24, 33 One randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial demonstrated a 26% decrease in hot flash frequency (P = .045 clonidine vs placebo) in patients with breast cancer. Both oral clonidine and gabapentin are effective in obtunding pressor response to direct laryngoscopy, clonidine being better in terms of controlling HR. Gabapentin produces more postoperative sedation than clonidine. In our study, we found that both clonidine and gabapentin are effective premedicants by oral route 2 h before induction of anesthesia to blunt the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation as compared to placebo. According to this research results, clonidine + gabapentin can reduce neuropathic pain and the severity of neuropathic pain in diabetic patients. Therefore, it is recommended that healthcare professionals with diabetes expertise prescribe these medications to reduce neuropathic pain and its severity. Compare Clonidine vs Gabapentin head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Conclusions: Premedication with oral clonidine (150mcg) or gabapentin (300mg) effectively attenuates intraoperative hemodynamic changes, reduces PONV incidence, and provides better post-operative pain relief compared to placebo in patients undergoing middle ear surgeries. Clonidine showed superior results compared to gabapentin. Compare the effectiveness of clonidine vs. gabapentin for generalized anxiety disorder in adults based on the experiences of 536 members of the generalized anxiety disorder in adults research community.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |