Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
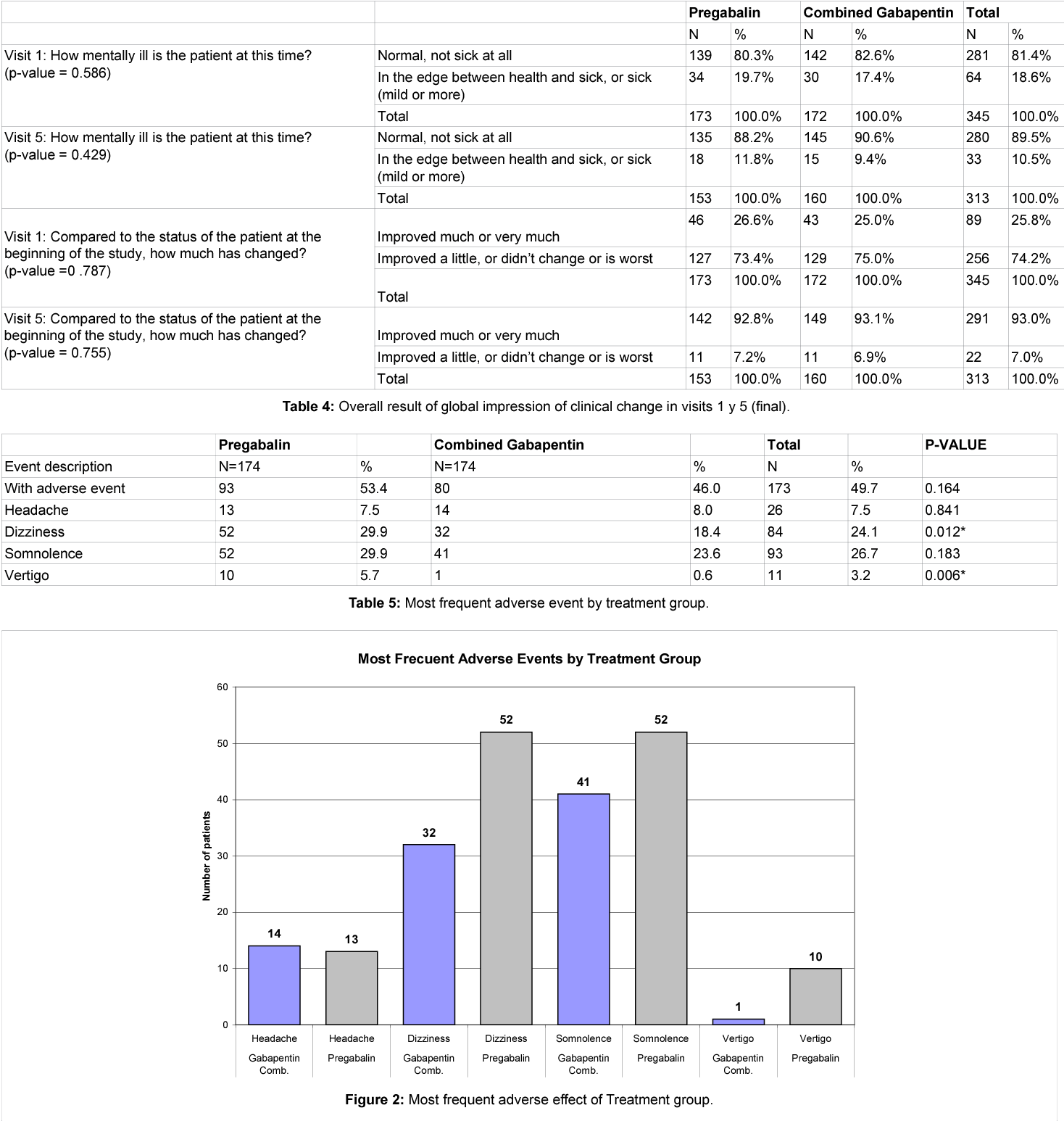 |  |
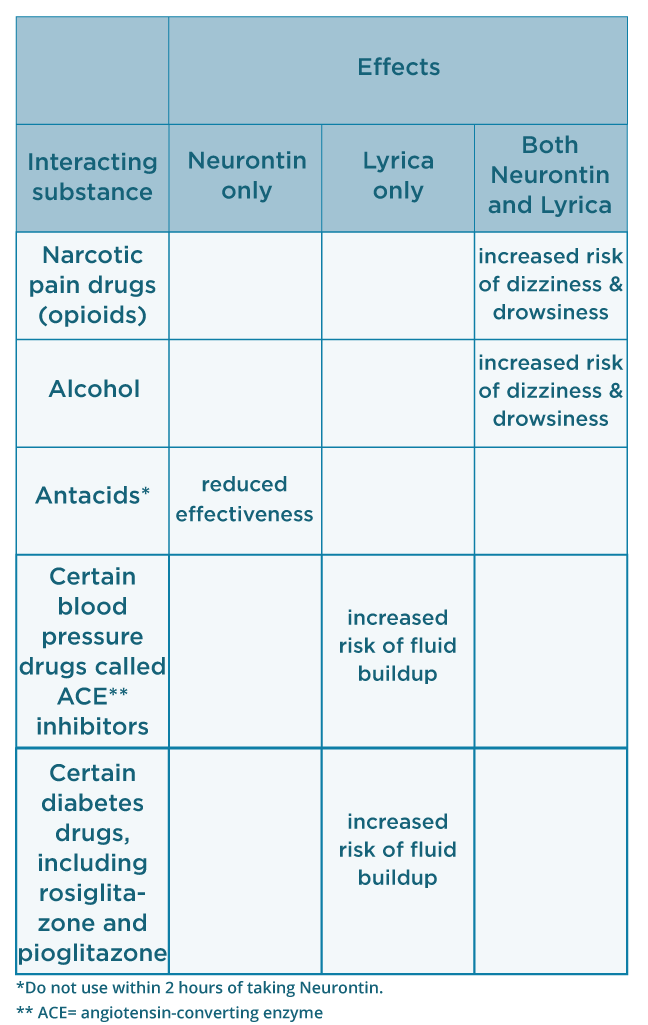
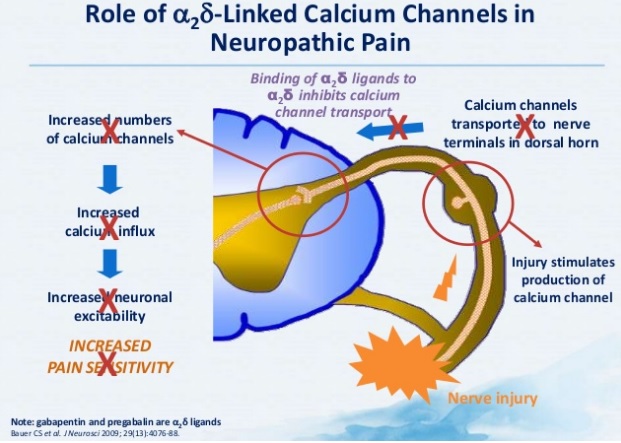
Although pregabalin and gabapentin share similarities in their mechanisms of action, they exhibit some pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic differences. In terms of pharmacokinetics, pregabalin demonstrates higher oral bioavailability, faster absorption, and a more predictable dose-response relationship than gabapentin (6, 7). I now advocate for deprescribing gabapentin when patients do not achieve adequate pain relief for chronic neuropathic pain at a cumulative daily dose of 1800 mg. Instead, I consider pregabalin as a substitute for gabapentin in patients with inadequate pain control rather than further dose escalations. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diabetes mellitus who are treated in the office setting and significantly affects quality of life. It typically Pregabalin has more FDA approvals for neuropathic conditions than gabapentin. Both are approved for postherpetic neuralgia and seizures. Pregabalin is authorised to treat neuropathic pain resulting from spinal cord injury, fibromyalgia, and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are recommended as the first-line treatment for neuropathic pain due to SCI [18, 19]. Both drugs have been shown to be effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain due to postherpetic neuralgia [20 – 26] and diabetic peripheral neuropathy [24 – 29]. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate and compare the effectiveness and safety of pregabalin vs. gabapentin in managing neuropathic pain. Methods: This study followed PRISMA guidelines and employed the PICOS search strategy. While gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) share many similarities, there are a few things that set them apart. We’ll highlight seven key differences between these medications below. 1. Pregabalin is FDA approved for more uses than gabapentin, but both are often used off-label. Gabapentin is not the same as pregabalin, even though they both belong to the same class of medicine, called gabapentinoids, and work similarly. Lyrica and Lyrica CR are the only brands of pregabalin. Neurontin is a brand name for gabapentin. Other brands of gabapentin include Gralise and Horizant. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both effective treatments for neuropathic pain and other conditions, but they differ in several key aspects. Pregabalin has faster absorption, onset of action, and greater potency, making it more effective for some patients. As an antiepileptic, pregabalin may be more effective than gabapentin in reducing the seizure frequency 4. In the treatment of neuropathic pain pregabalin has been shown in studies to provide equivalent efficacy to gabapentin, however, at much lower doses. Millions of people suffer from the burning, tingling, and numbness of a form of neuropathy called idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. A recent study directly comparing four medications produced disappointing results, but is a step in the right direction. Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate and compare the effectiveness and safety of pregabalin vs. gabapentin in managing neuropathic pain. Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Pregabalin is a first-line treatment in all major international guidelines on the management of painful diabetic neuropathy (pDPN). Treatment with pregabalin leads to a clinically meaningful improvement in pain scores, offers consistent relief of The anticonvulsants pregabalin and gabapentin are both indicated for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain. The decision on which treatment provides the best alternative, should take into account all aspects of costs and outcomes associated Neuropathic pain is a prevalent and burdensome condition, and both pregabalin and gabapentin are widely used for its treatment. However, there is a lack of clarity regarding their comparative efficacy and safety. Both pregabalin and gabapentin are antiepileptic medications that bare structural resemblance to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though neither agent has activity in GABA’s neuronal systems. Gabapentin is also used to treat nerve pain caused by shingles (herpes zoster). Other uses for Lyrica are neuropathic (nerve) pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia. Both gabapentin and Lyrica may interact with alcohol and drugs that cause sedation including narcotic pain medications. A prospective, randomized, open label, 12-week study that compared the safety and efficacy of gabapentin, duloxetine, and pregabalin in 152 patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |