Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
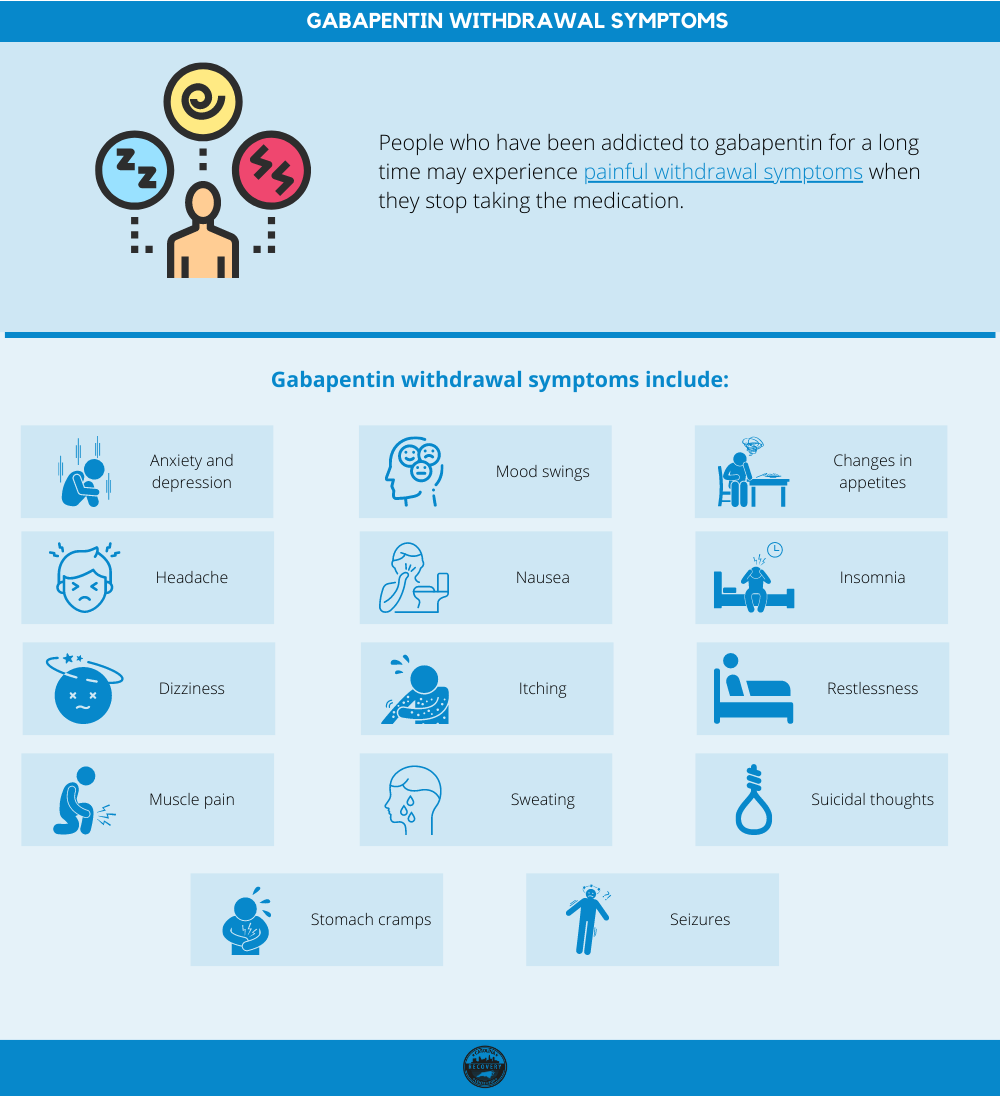
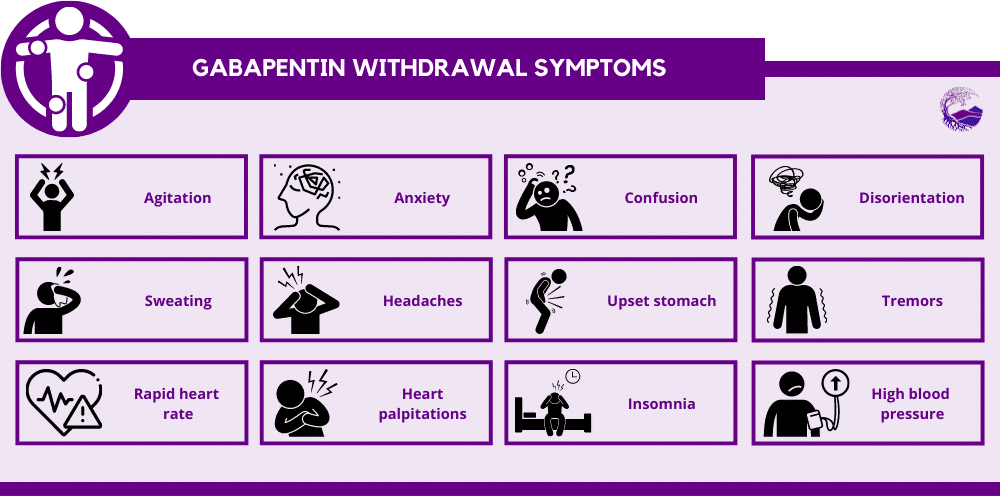
Gabapentin is a prescription drug commonly used to treat nerve pain, seizures, insomnia, alcohol withdrawal, and alcohol use disorder. Once considered a safe and non-addictive option, it gained widespread use for chronic pain and neurological conditions. In 2017 alone, 68 million prescriptions for gabapentin were written, making it one of the top ten most prescribed medications in the United Gabapentin withdrawal can cause symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, nausea, sweating, and seizures in severe cases. Withdrawal typically begins within 12-24 hours after stopping the drug and can last up to 10 days. Consult your doctor before you stop taking gabapentin. Never stop taking this medication all at once. Your doctor can help develop a plan to help you taper off. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety, depression, headaches, insomnia, and a general feeling of malaise. If you’re planning to stop taking Gabapentin, it’s best to taper your dosage slowly with the help of your doctor. Insomnia is one of the early symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal and can last for several days or weeks. When GABA levels drop due to drug use cessation, it can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, dizziness, sweating, and increased heart rate. In more severe cases, seizures are a known risk, particularly for individuals using gabapentin to manage epilepsy. Withdrawal symptoms of gabapentin include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, sweating, headaches, and irritability. In severe cases, individuals may experience confusion, muscle pain, or seizures. How can I avoid gabapentin withdrawal? The best way to avoid gabapentin withdrawal is to only take the dose prescribed by your doctor, for the shortest time possible. When it comes time to stop it, talk to your healthcare provider about a tapering schedule. Do not misuse substances or alcohol while you are taking gabapentin. What is gabapentin used for? Gabapentin is a prescription medication Gabapentin withdrawal can trigger sleepless nights, leave you feeling on edge, and cause a surge in nerve pain or anxiety, making it tough to tell what’s really happening. Discontinuing gabapentin can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has become increasingly popular over the years. While it can be effective in managing certain conditions, many individuals find themselves questioning the implications of stopping this drug. Understanding what happens when Gabapentin is a prescription anticonvulsant medication that’s used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions that involve the nerves. It may also be used to treat alcohol withdrawal and insomnia. Gabapentin misuse and abuse are reported, though not commonly, with the potential for physical dependence and severe withdrawal symptoms if abruptly discontinued. Learn more [] Gabapentin withdrawal can be a challenging and uncomfortable process, with both physical and psychological symptoms that vary in intensity. Whether you’re dealing with anxiety, insomnia, digestive issues, or more severe concerns like seizures and depression, professional support is crucial to ensure a safe and effective recovery. Gabapentin withdrawal can cause various symptoms, including anxiety and insomnia, when stopping the medication abruptly. Gabapentin withdrawal isn’t always easy. Here is everything you need to know about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms, your timeline, and how to get help. Insomnia, dizziness, fatigue, muscle pain, headaches, and loss of appetite are some of the symptoms related to gabapentin withdrawal. Read this HealthHearty article to know how long the withdrawal process lasts. These might include anti-seizure medications other than gabapentin to prevent withdrawal seizures, anti-anxiety medications for short-term use during acute withdrawal, sleep aids to address insomnia and sleep disturbances, and medications to manage nausea, headaches, or other physical symptoms. Learn about the potential side effect of insomnia when stopping the use of gabapentin and how to manage it. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug prescribed for seizures and nerve pain. People who develop physical dependence to gabapentin may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to come off it. Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms may include insomnia, rebound pain, and flulike symptoms. Learn more about the symptoms, timeline, and treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |