Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 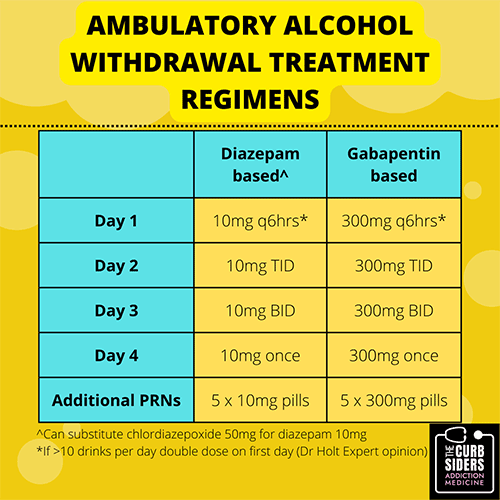 |
Does gabapentin cause withdrawal? Learn more about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms, when they occur, and what can help. A person who wants to stop taking gabapentin should first talk with their doctor to minimize withdrawal symptoms and manage any side effects. Learn more here. The risks of withdrawal are higher if you’re taking high doses or have been on gabapentin for longer than 6 weeks. Withdrawal symptoms can start from 12 hours to 7 days after stopping the From anxiety to seizures, gabapentin withdrawal can be serious. Get informed on symptoms, timelines, and expert-recommended tapering methods. The MHRA and manufacturers advise that when prescribing gabapentin in patients who require concomitant treatment with opioid medicines, patients should be carefully observed for signs of CNS depression, such as somnolence, sedation, and respiratory depression, and the dose of either gabapentin or the opioid should be reduced appropriately.6,7 When discontinuing gabapentin (Neurontin), withdrawal symptoms can occur, so a gradual dose reduction is recommended. Read here for side effects, timeline, and treatment for gabapentin withdrawal. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug for seizures and nerve pain. Learn more about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms and how to safely stop taking the medication. In our latest question and answer, we discuss how to safely stop taking gabapentin, by slowly lowering your dose to prevent withdrawal. Gabapentin withdrawal isn’t always easy. Here is everything you need to know about gabapentin withdrawal symptoms, your timeline, and how to get help. How long does gabapentin withdrawal last? Learn what to expect with withdrawal, including timeline, symptoms, and how to safely taper off gabapentin. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, confusion, and rapid heart rate. Learn more about the symptoms, timeline, and treatment. A comprehensive guide to safely stopping gabapentin, managing withdrawal symptoms, and addressing withdrawal-induced depression. Seek professional help throughout the process. A structured gabapentin taper chart helps ease withdrawal and minimize risks, but knowing what works—and what doesn’t—matters just as much. Learn more. Gabapentin is used to treat seizures and nerve pain but has the potential for misuse. Learn about gabapentin withdrawal and tapering strategies. A comprehensive guide to creating a safe and effective withdrawal schedule for gabapentin, including tips for managing withdrawal symptoms and tapering off the medication. Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. See tables 1 through 5 for case reports describing gabapentin tapers. How can I avoid gabapentin withdrawal? The best way to avoid gabapentin withdrawal is to only take the dose prescribed by your doctor, for the shortest time possible. When it comes time to stop it, talk to your healthcare provider about a tapering schedule. Do not misuse substances or alcohol while you are taking gabapentin. What is gabapentin used for? Gabapentin is a prescription medication Find guidance on gabapentin withdrawal, symptoms, and options for detox. Learn how to stop taking gabapentin and manage the withdrawal process effectively. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms and their intensity can depend on how high of a dose you take, how long you’ve taken it, and how you taper off of it. Gabapentin is a non-controlled medication most often prescribed to prevent seizures or treat nerve pain. Recently, misuse and abuse of gabapentin have increased, leading some states to regulate [] Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms may include insomnia, rebound pain, and flulike symptoms. Learn more about the symptoms, timeline, and treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |