Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
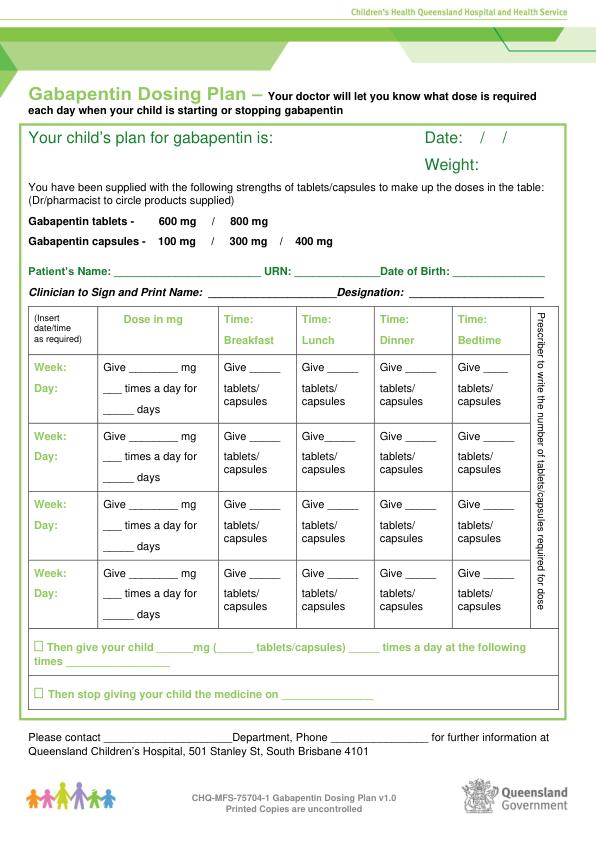 |  |
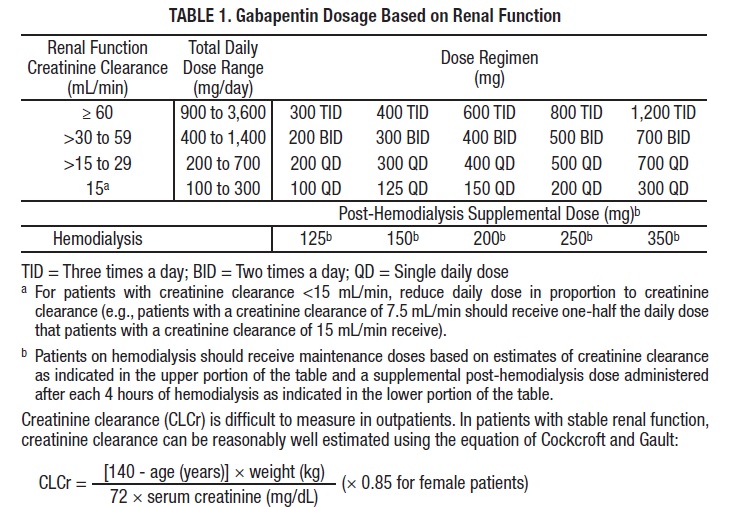
In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue [1] Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years <3 years: Safety and efficacy not established Abstract Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug, which in man is cleared solely by renal excretion and is not bound to plasma proteins. Because the clearance of gabapentin is dependent on renal function, the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin were investigated in anuric subjects maintained on hemodialysis. Plasma samples were obtained over an 8-day period after administration of single oral 400-mg Introduction Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1).1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Dose as in GFR=15–30 mL/min Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAntacids: reduce absorption Antidepressants: antagonism of anticonvulsive effect (convulsive threshold lowered) Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators. Recommended Therapeutic dosing targets of both medications have been established in clinical trials for neuropathic pain (gabapentin 1800–3600 mg/day; pregabalin 150–600 mg/day). Detailed dosage guidelines and administration information for Neurontin (gabapentin). Includes dose adjustments, warnings and precautions. Dose adjustment and avoidance of certain analgesics may be required in patients with advanced CKD and ESRD. We review the available evidence on pharmacokinetics and adverse drug effects of various analgesic agents commonly used in patients with advanced CKD and ESRD. The recommended dosing in ESRD for gabapentin is 300 mg and for pregabalin is 75 mg, administered once a day [25]. The aforementioned dosing recommendations are based on population-based pharmacokinetic data and not on actual clinical trials. The recommended dose of gabapentin in dialysis patients is 100 to 300 mg/per day, but on dialysis day an additional dose is given after the session, due to drug clearance through the dialysis membrane. 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Many analgesics that are typically used in the non-CKD population should not be used among patients with advanced CKD (ie, estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2; including those on dialysis). This topic reviews the epidemiology, assessment of pain, and management of pain among patients with advanced CKD. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost Gabapentin Dosage Guidelines in Adults, Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older with Renal Impairment 1-5. The clearance of both gabapentin and pregabalin decreases and half-life (t ½) increases proportionately with worsening renal function, requiring renal dose adjustment (Tables 1 and Supplementary Table 1) [106 - 108]. Both medications should be dosed post-HD. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal impairment: In this scenario you are carrying out an audit of gabapentinoid prescribing in your work area, to ensure that the doses prescribed in renal impairment are safe and appropriate. For adults with normal kidneys: Nerve Pain/Restless Leg Syndrome: Start 300 mg once daily, increase to 300 mg 3 times a day. Max: 3600 mg per day. Seizures: Start with 300 mg 3 times a day, then increase to 600 mg 3 times a day. 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |