Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
/male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5aa15ae80e23d90037526254.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
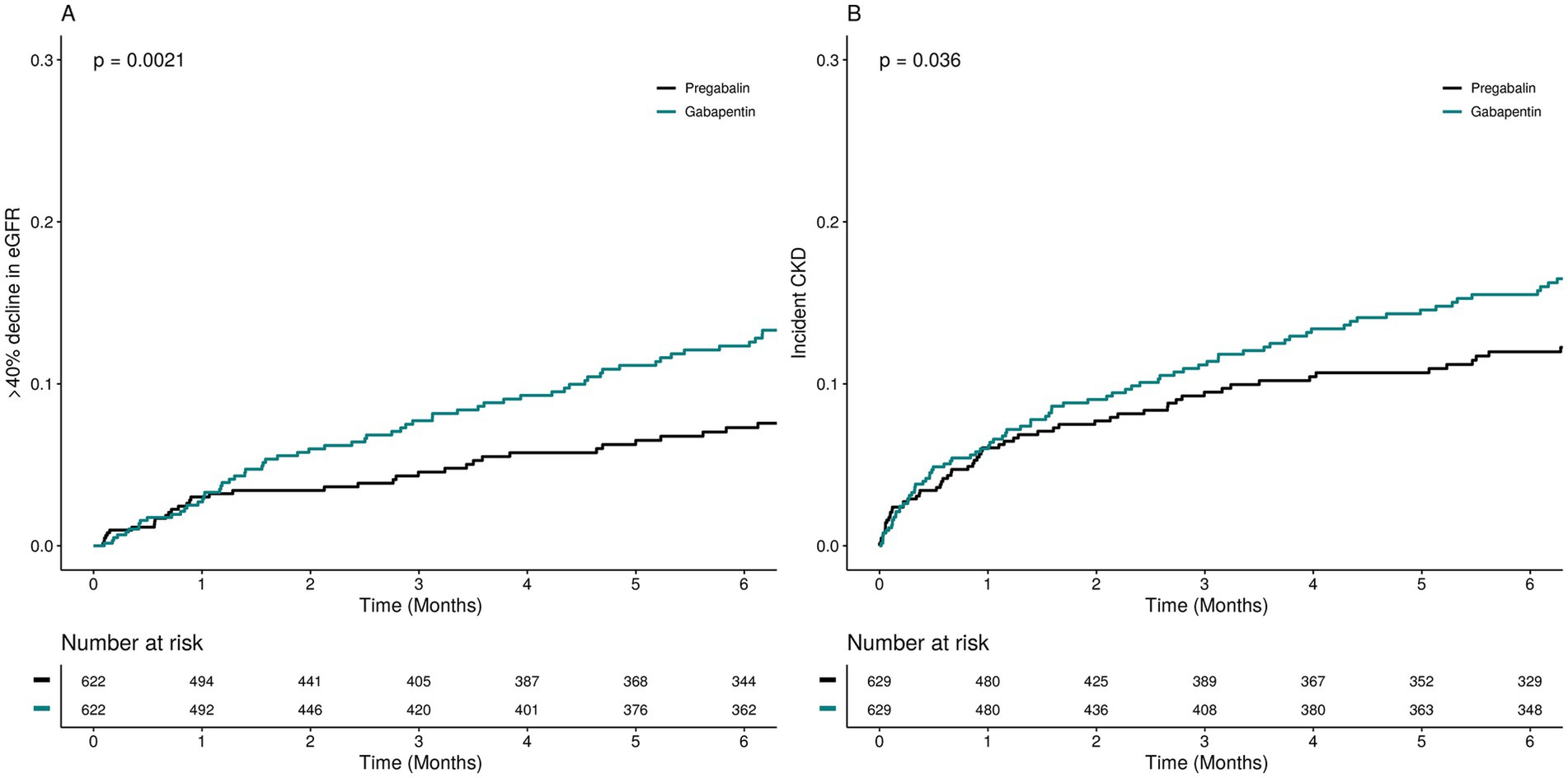 |  |
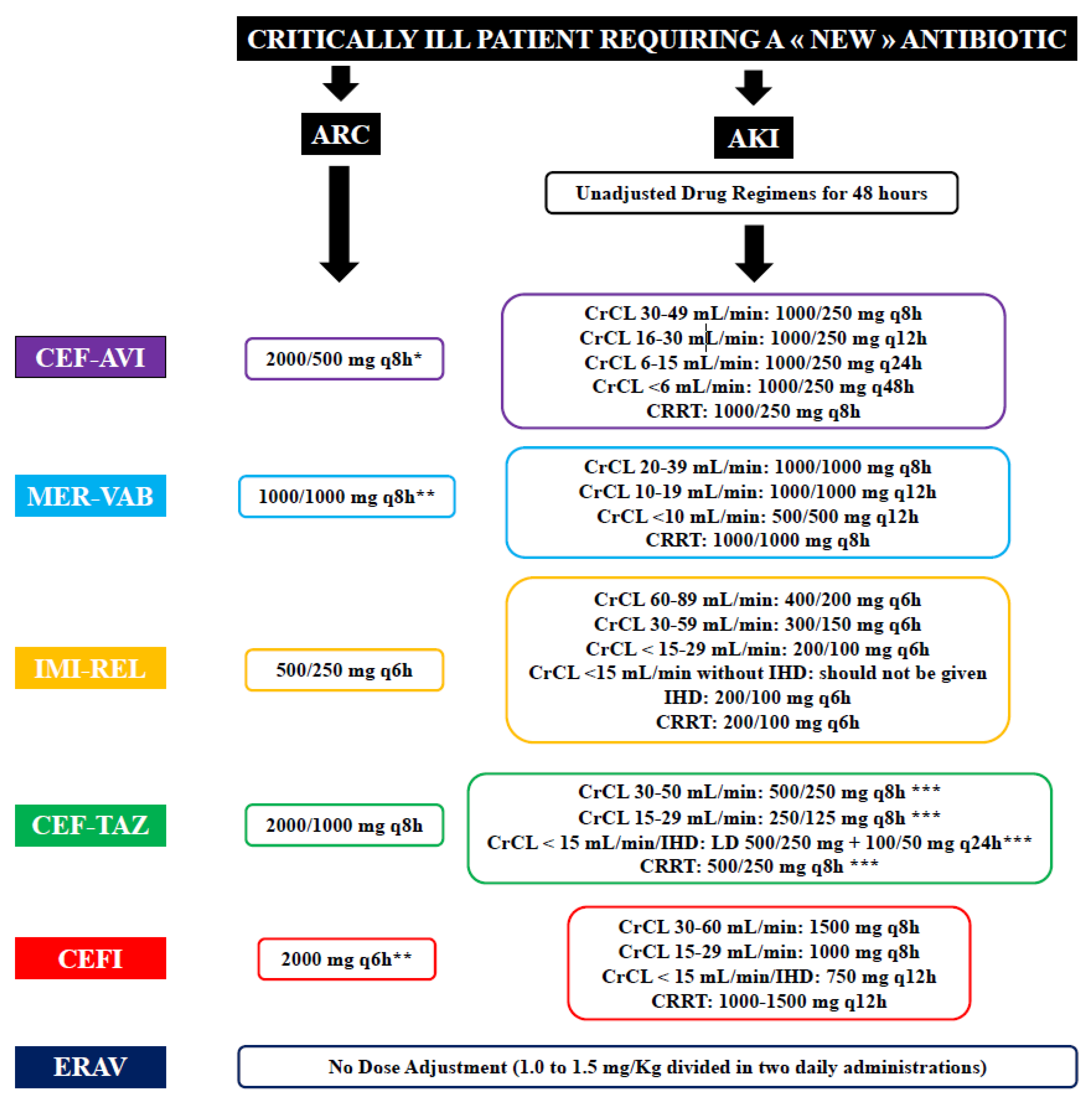
Gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in patients with CKD primarily to treat neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome and given the high prevalence of diabetes in this population, the proportion who receive these drugs is very high. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia pain associated with shingles, restless leg syndrome, and diabetic neuropathy. For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. In elderly patients, and in patients with impaired renal function, Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has no harmful effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin and pregabalin are used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but require renal adjustments. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that results from an age-related decrease in renal function. Abstract Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related adverse events (GRAEs). Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis Introduction Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1).1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed as opioid alternatives. Given that gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body by the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. INTRODUCTION Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [1]. The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [2-9]. Among hemodialysis patients, severe pain is also independently associated with shortened or missed Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Major Gabapentin (applies to Neurontin) renal dysfunction Major Potential Hazard, High plausibility. Gabapentin is primarily eliminated unchanged by the kidney. Therapy with gabapentin should be administered cautiously in patients with impaired renal function.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
/male-kidney-anatomy--illustration-758313113-5aa15ae80e23d90037526254.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |