Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 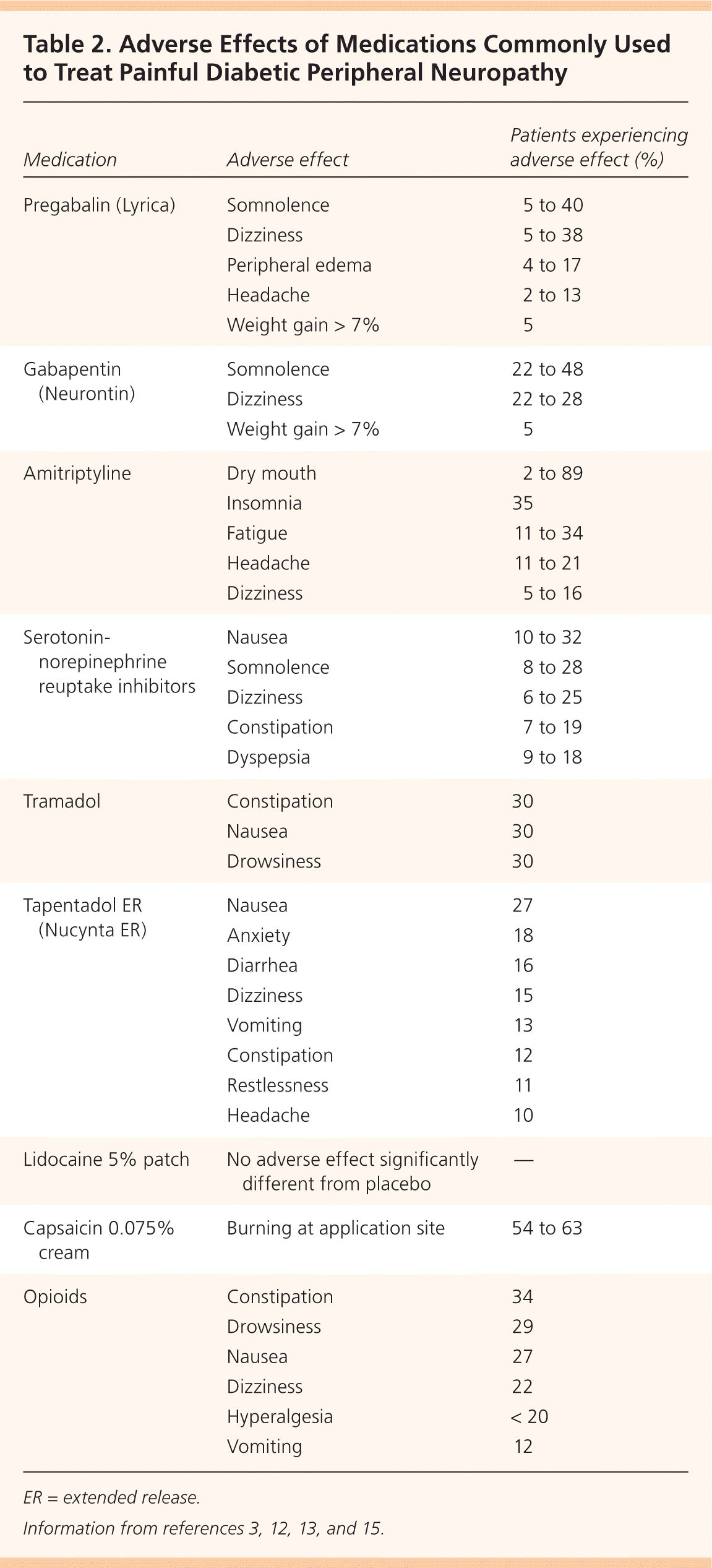 |
Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other neuropathic pain syndromes. It relieved symptoms of allodynia, burning pain, shooting pain, and hyperesthesia. Adverse effects were typically mild to moderate and usually subsided within approximately 10 days from the initiation of treatment. It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). Medicines such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, often improve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness. Yes, there are reports suggesting a possible link between gabapentin and peripheral neuropathy in some individuals. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has garnered attention for its potential side effects. One of the more concerning discussions revolves around whether gabapentin may contribute to the development of peripheral neuropathy. This condition Medical Indications In animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diabetes mellitus who are treated in the office setting and significantly affects quality of life. It typically In the 2016 report, most of the available randomized control trial (RCT) data pertained to diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), it was concluded that for DPN there was greater reduction in neuropathic pain and increased risk of adverse events associated with gabapentin compared with placebo. Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, easily titrated, has few drug interactions, and does not require laboratory monitoring. Patients suitable for gabapentin should have a clear neuropathic pain syndrome, characterized by sharp, shooting, lancinating and/or burning pain, in a nerve root (radicular) or stocking/glove distribution. Gabapentin for Adults With Neuropathic Pain: A Review Key Messages Overall, evidence suggests that there is a greater reduction in neuropathic pain (NP) with gabapentin compared with placebo in adults who have a variety of conditions, including diabetic peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. US marketing approval for gabapentin was granted in 2002 for postherpetic neuralgia; in Europe, the label was changed to include peripheral neuropathic pain in 2006. Gabapentin has the trade name Neurontin TM, and is also available as generic products in some parts of the world. Gabapentin has a half‐life of five to seven hours. Gabapentin is a medication originally developed to treat seizures but has since become a go-to for nerve-related pain, including peripheral neuropathy. It works by inhibiting certain nerve signals, effectively reducing pain sensations. The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. Check whether Peripheral neuropathy is associated with a drug or a condition. On Apr, 08, 2025 313,421 people reported to have side effects when taking Gabapentin. Among them, 123 people (0.04%) have Peripheral neuropathy. Pain expert offers clinical guidance to a commonly asked question about the proper, safe, and effective dose of gabapentin when treating neuropathic pain. 301 Moved Permanently301 Moved Permanently cloudflare A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak [60]. A gastroretentive gabapentin formulation for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: efficacy and tolerability in a double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. A Doctor’s Insight into Nerve Pain Management If you’re dealing with nerve pain from conditions like peripheral neuropathy, sciatica, or diabetic nerve damage, you may have been prescribed gabapentin to manage your symptoms. But a question that frequently comes up among patients is: Does gabapentin help heal nerve damage, or does it just mask the pain? As a doctor specializing in treating Millions of people suffer from the burning, tingling, and numbness of a form of neuropathy called idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. A recent study directly comparing four medications produced disappointing results, but is a step in the right direction.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |