Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
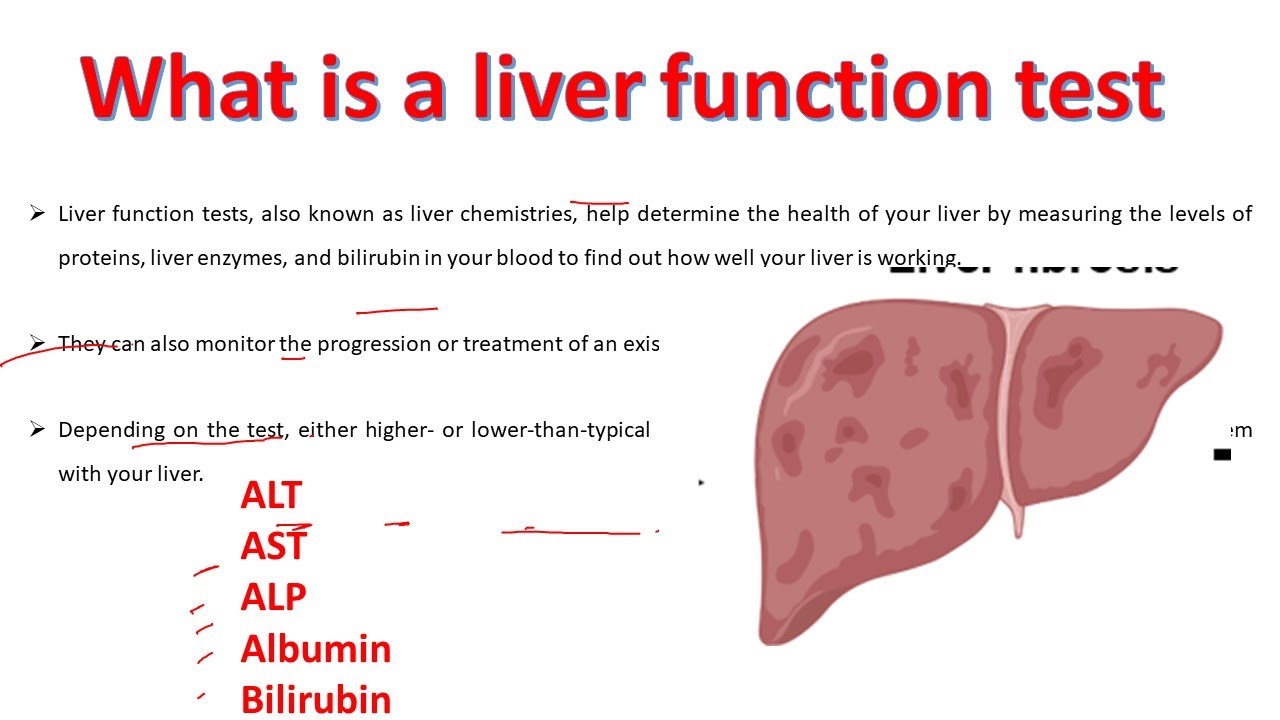
Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults and the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn about side effects, drug interactions, dosages, warnings, and more. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. After taking the gabapentin for two weeks he developed the clinical characteristics of cholestasis—namely, jaundice, dark urine, pale stool in association with fatigue, and epigastric tenderness. Familial non-hemolytic-non-obstructive jaundice (jaundice without evidence of liver damage, biliary obstruction) is found to be associated with 2 drugs and 5 conditions by eHealthMe. The man developed liver problems after taking the drug for two weeks, according to the case report. Symptoms included dark urine, jaundice, pale stool, fatigue and upper abdominal tenderness. After the man quit taking gabapentin, his liver function test and symptoms gradually improved. Pruritus is associated with multiple cholestatic disorders, including primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and inherited p Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range of doses Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Identify the type of seizure that does not involve motor convulsions. Atonic seizure Myoclonic seizure Absence seizure Partial seizure, Describe the difference between anticonvulsant drug agents and antiepileptic drug agents., Why is the additional administration of diazepam (Valium) required to control seizures in the treatment Purpose: Trazodone and gabapentin are commonly used treatments. We report a rare case of trazodone and gabapentin-induced liver injury. Case: A 40-year-old woman with a history of depression presented jaundice. She had no other complaints. The patient denied risk factors for acute and chronic liver disease. She had been taking trazodone 50 mg daily for the past 5 years. The only concomitant Drug induced cholestasis may present as an acute illness that promptly subsides with the withdrawal of the offending agent. It may present with or without jaundice. However, parenchymal liver injury may elicit non-specific symptoms like nausea, malaise, anorexia and fatigue. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin has been associated, rarely, with jaundice. It is not safe to take gabapentin without a prescription. It is also dangerous to take gabapentin with alcohol and some other drugs. Alcohol and some drugs depress the central nervous system, which affects a person’s breathing. The drugs that do this include: Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Check with your doctor right away if you have a fever, rash, swollen, painful, or tender lymph glands in the neck, armpit, or groin, unusual bleeding or bruising, or yellow eyes or skin. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1,800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range After taking the gabapentin for two weeks he developed the clinical characteristics of cholestasis—namely, jaundice, dark urine, pale stool in association with fatigue, and epigastric tenderness. Physical examination confirmed jaundice and the previously noted retinopathy and neuropathy. Gabapentin tablet contains gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. Gabapentin's chemical name is 1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Jaundice - yellow skin is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Paracetamol, and have Multiple sclerosis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |