Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
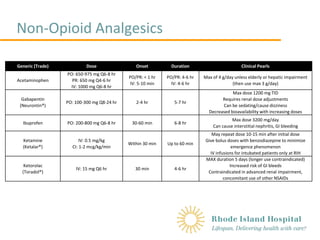
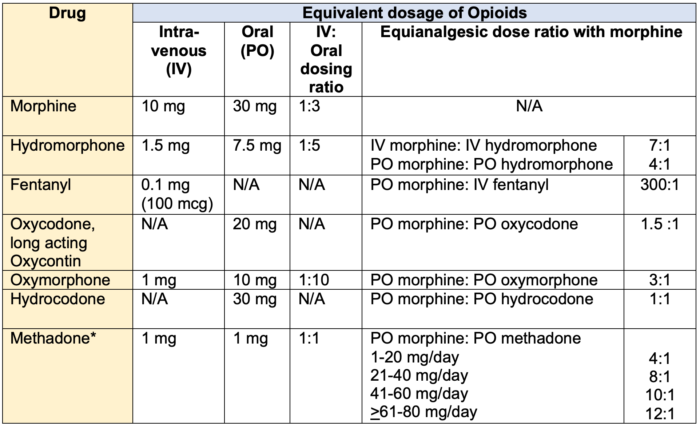
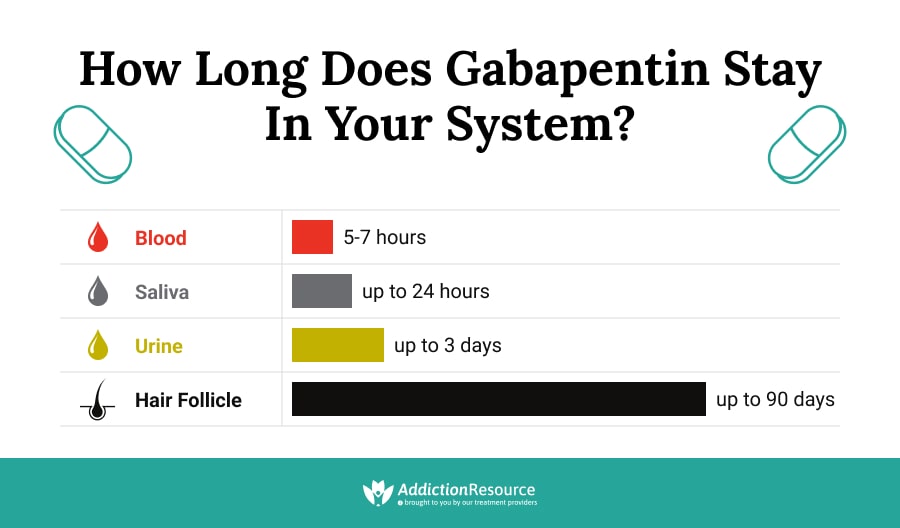
Absorption and distribution Pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed as compared to gabapentin. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed ^In elders, use a bulk laxative and give instructions regarding activity, hydration and close follow-up General Opioid Analgesics Chart Gabapentin's duration in the body depends on several factors, including dosage, individual metabolism, and liver and kidney function. Generally, peak blood levels occur within 2-3 hours after oral administration, with a half-life of about 5-7 hours. This means that about half of the drug is eliminated from the body every 5-7 hours. The elimination process primarily occurs through the kidneys May affect transport of amino acids across neuronal membranes Onset & Peak Onset: Unknown Peak IR:2-4 Hrs, ER: 8 hrs Encarbil:5-7.3 hrs Indications Neuropathic pain Postherpetic neuralgia Moderate to severe restless leg syndrome Treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization in patients with epilepsy Drug Library safe Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has gained attention for its effectiveness in various medical scenarios. Understanding how long it takes gabapentin to take effect is crucial for anyone considering this medication. The onset of action can vary based on several factors, including dosage, individual metabolism, and the condition being treated. When Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used in the prevention of partial seizures. It is frequently used for neuropathic pain including diabetic neuropathy, radiculopathy, shingles, and trigeminal neuralgia. Two hours after your first dose of in your case (300mg)and then it grows from there. Peak Plasma levels are reached at three hours. Quick onset of action times found within this table may account for the drug’s absorption in the oral liquid form. Onset of action can also differ due to the manufacturer’s variability with tablet compression effecting disintegration and dissolution times when ingested. Gabapentin Tablets, USP are indicated for: Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults - Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Gabapentin Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on June 18, 2024. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific Objective: Gabapentin immediate release (GBP-IR), gabapentin gastric retentive (GBP-GR), and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil extended release formulation (GEn) have been approved for management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in adults. This is the first pharmacokinetic (PK) comparison of all three formulations using FDA-recommended doses for PHN. Gabapentin typically takes 1 to 2 hours to start working, but full effects may take several days to reach. Gabapentin, often prescribed for neuropathic pain, seizures, and restless leg syndrome, has become a common choice for many seeking relief. Understanding how long it takes for gabapentin to take effect is crucial for those using it for the first time or adjusting their dosage. The onset The peak plasma concentration for gabapentin is 2 to 4 hours. The time to peak plasma concentration for gabapentin enacarbil is 5 hours for subjects in a fasting state and 7.3 hours for under-fed conditions. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. What you will learn Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that’s used to treat seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin has a half-life of 5 to 7 hours, but it can vary by dosage, formulation, and individual factors. Gabapentin’s half-life and how long it stays in the body influence how long the effects last and possible risks. How long does it take for gabapentin to kick in? Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with maximum plasma concentrations attained within 3-4 hours. When used to treat a type of seizure disorder, called a partial onset seizure, gabapentin decreases the abnormal activity in the brain that causes the seizures. When used to treat nerve pain, or neuralgia, following a herpes zoster (shingles) infection, gabapentin may reduce the response to painful stimuli. Neurontin (gabapentin) has a short half life of 5 to 7 hours and a short duration of action of 6 to 8 hours.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |