Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
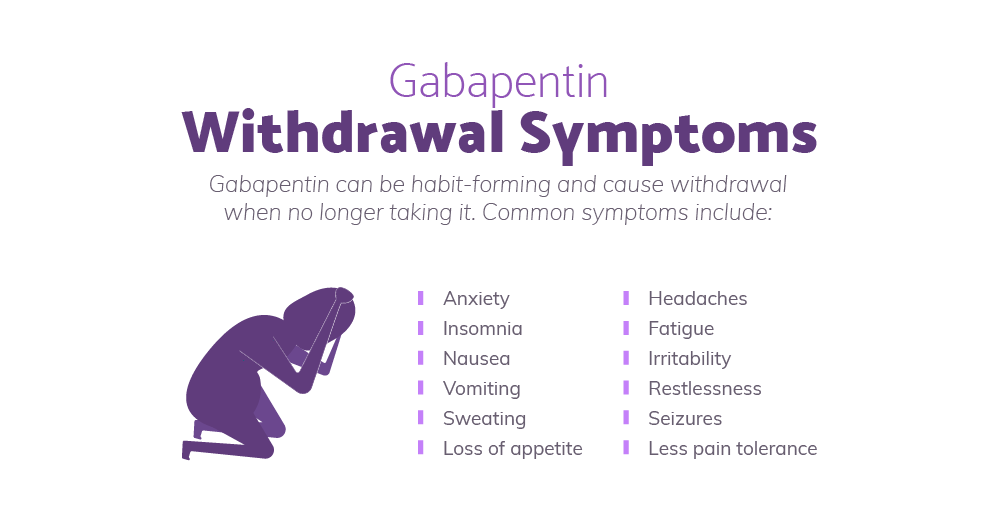
Gabapentin (Neurontin) is prescribed for epilepsy and nerve pain, but some people may take gabapentin for sleep. Learn about whether off-label gabapentin works for sleep disorders. Highlights Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that is primarily used to treat seizures, but it can be used off-label as a sleep aid. Gabapentin can reduce nighttime awakenings and promote more slow-wave sleep. There is a risk of misuse and dependence on gabapentin, which leads to potential concerns regarding its long-term use. The optimal use of gabapentin for sleep involves careful consideration of timing, dosage, and integration with good sleep hygiene practices. Typically, taking gabapentin 1-2 hours before bedtime allows for its sleep-promoting effects to align with the desired sleep onset. Gabapentin addiction: Learn about the potential for dependence, recognize withdrawal symptoms, and discover treatment options. In other studies, it appears that gabapentin may improve sleep in people with other medical conditions that make it more difficult to sleep, such as alcohol dependence, hot flashes and bipolar disorder. In a large review of 26 studies on gabapentin and sleep in patients with other medical conditions, the average dose taken daily was about 1,800 mg. Similarly, Gabapentin vs Xanax for Sleep: Comparing Effectiveness and Safety is another comparison worth considering. Xanax (alprazolam) is primarily an anti-anxiety medication that can also help with sleep, but it carries a higher risk of dependence and more severe withdrawal symptoms compared to gabapentin. Special Considerations and Precautions Gabapentin is a generic drug used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It's not an opioid but is it addictive? Learn about gabapentin addiction versus dependence and more. Additionally, while gabapentin is commonly prescribed off-label for sleep issues, this practice raises important concerns about its long-term safety and potential for dependency. The effects of prolonged use are still being studied, and patients may not fully understand the implications of taking gabapentin regularly for sleep. Gabapentin is an established pharmaceutical used to treat seizures and pain. Gabapentin is safe and well-tolerated when used as prescribed. However, misuse has skyrocketed among recreational and dependent opioid users to enhance effects and relieve withdrawal. Combined gabapentin and opioid use comes with a substantial risk of overdose and death. Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions like anxiety. While it is often effective for its intended uses, prolonged use or misuse of gabapentin can lead to dependency and withdrawal symptoms when discontinued. Gabapentin withdrawal is an important issue to understand, especially for individuals who have been on the medication long-term Key Takeaway While gabapentin may improve sleep quality in the short-term, its long-term effects on sleep architecture and potential for dependence require careful consideration and monitoring by healthcare professionals. Gabapentin is a prescription Painkiller that is less addictive than Opioids. Still, addiction and abuse occur; overdosing is possible. How Do You Develop A Dependence On Gabapentin? Taking gabapentin long-term is enough to develop a physical dependence on this type of medication. If you are taking gabapentin for a chronic condition such as epilepsy, your doctor can help you judge whether the potential for a physical dependence outweighs the symptoms it treats. In today’s video, we explore the off-label uses of Gabapentin, also known as Neurontin. While Gabapentin is FDA-approved for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, its off-label uses are more extensive, especially in psychiatry. Intro Gabapentin is a medication that has garnered attention for its potential role in sleep disorders. Initially developed to treat epilepsy, it has found varied applications, including pain management and anxiety relief. An increasing number of individuals are exploring its efficacy for sleep-related issues. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of gabapentin dosage Gabapentin presents a dual narrative in insomnia management. The effectiveness of this medication in promoting better sleep must be continuously scrutinized against its possible side effects. The delicate balance between achieving relief from insomnia through gabapentin and managing its risks is critical for healthcare practitioners. Gabapentin addiction refers to the misuse of prescription for non-medical purposes. Learn the signs, withdrawal symptoms, & treatment. Conditions such as insomnia, restless leg syndrome, and sleep apnea affect millions of individuals worldwide, leading to significant impairments in daily functioning and overall quality of life. As traditional sleep aids often come with a host of side effects and dependency risks, gabapentin presents a compelling alternative that warrants thorough exploration. This article delves into the Inferiority: While there’s one study suggesting that gabapentin may be superior to trazodone for the treatment of alcohol dependence-related insomnia, it’s possible that gabapentin is an inferior intervention as compared to first-line hypnotics for the management of sleep disorders.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |